-
Faculty of Science, Department of Zoology
- Professor
- Kazuyuki MEKADA
- Research Field
Laboratory Animal Science, Experimental Zoology
- Keyword(s)
Animal breeding and genetics
- Research theme
-
- Characterization of wild-derived animals
- Establishment and analysis of novel animal disease models
- Genetic background monitoring of laboratory mice
Outline of research activities


We investigate various biological characteristics such as genetics, morphology, physiological reproduction, and nutrition of wild animals, especially small mammals, through breeding and preservation of their breeding stock (e.g., suncus and voles). To elucidate the diverse biosystems in humans and other animals, we aim to create unique animal resources that enable us to obtain knowledge that is difficult to obtain with common laboratory animals (e.g., mice and rats) and to improve their added value.
- Desired cooperation
-
- Development of techniques for genetic monitoring of laboratory animals,
- Analysis of animal disease models, etc.
-
Faculty of Science, Department of Zoology
- Professor
- Shinya MIZUNO
- Research Field
Regenerative Medicine, Biochemistry, Physiology
- Keyword(s)
Growth Factor, Intracellular Signaling Pathway, Gene Expression, Environmental Adaptation
- Research theme
-
- Molecular basis for HGF-mediated organogenesis
- Molecular basis for HGF-mediated organogenesis
- Basic study on HGF-based self repair therapy of intractable diseases
- Molecular analysis of vertebrate's adaptation to severe winter or drought stresses
Outline of research activities

Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) was originally identified as an hepatotrophic factor. During the past 30 years, we provided evidence to show that HGF plays an essential role for regeneration of several types of organs, including kidney, lung, hearts and neural tisses, using animal models of intractable disorders. HGF elicits unique biological activities, such as mitogen, motogen and morphgen via activating c-Met/HGF-receptor tyrosine kinase as shown below. Of note, a loss in HGF production is responsible for manifestation of acute and chronic organdiseases. This is the reason why HGF supplemental therapy produces benefit effects against the progression of acute and chronic organ diseases.
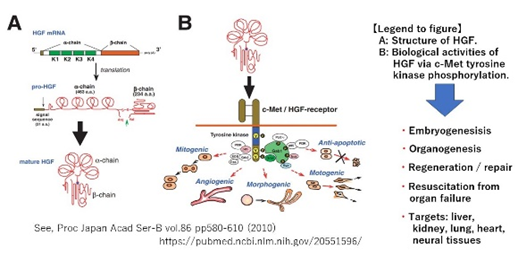
- Desired cooperation
-
- Practice of HGF-based self repair therapy in Vet.
- Renal repair, Tendon repair, lung regeneration
- Tissue engineering technique for HGF slow release
-
Faculty of Science, Department of Zoology
- Professor
- Shuji KOBAYASHI
- Research Field
Mammalogy, Systematic zoology, Primatology, Museology
- Keyword(s)
Myocastor coypus, Natural history, Phylogeny, Morphology
- Research theme
-
- Biology of Myocastor coypus
- Natural history of Myocastor coypus
- Behavioral characteristics of Cervs nippon
- General zoology in Okayama prefecture
Outline of research activitiesThe coypu (Myocastor coypus) is a large-sized rodent introduced from South America, and has been designated as a specific alian species since 2005 by Japanese government. However, the knowledge of its biological charateristics necessary for pest control is scanty. Thus, we are coducting related research on the coypu from various angles. We have revealed that the coypu has a high level of learning capability. It also has a high physical potential, such as climbing over a fence about 70 centimeters tall. In the historical aspect, we have also revealed that the background for the spread of the species in Japan has not been as has been told before. There was a nationwide campaign for promotion of the propagation of the coypu for meat production increase in the WWII postwar food shortage period.
- Desired cooperation
-
- Pest control of the nutria
- Pest control of the Japanese sika deer
-
Faculty of Science, Department of Zoology
- Professor
- Takahiro MURAKAMI
- Research Field
Evolutionary ecology, behavioral ecology
- Keyword(s)
Leaf-cutting ants, acoustic communication, anatomy, evolution, ecology, behavior
- Research theme
-
- Evolution of acoustic communication in ants
- Pest control and management of invasive alien species, such as fire ants
- FISH mapping of regeneration-related genes in amphibians and planarians
- A new fabric material development using ants and silkworms
Outline of research activities




The final goal of our research is to converse with ants. Ants have long been thought to engage in detailed communication using chemical substances such as pheromones. However, our researchis revealing that acoustic signals are also important toos of communication.We conducte detailed analyses of organs such as “ears” and “sound-producing organs”. It will be able to control the behavior of ants like leaf-cutting ants, which are significant damage against human society.
We have been collaborating with various stakeholders such as the Fukuoka City, Fukuoka Prefecture, and the Ministry of the Environment to control invasive alien ant species such as the red imported fire ant, the yellow crazy ant, and Argentine ant. In Okayama Prefcture, there have been reported of the little fire ant (Wasmannia auropunctata) at Mizushima Port, and we will continue to control and manage these ants.
By using silk produced by silworms, which domesticated in China 6,000 years ago, and the silks spun by black Japanese weaver ant in Okinawa, we conduct research to create new fabric sheets. We hope that as this research progresses, the black Japanese weaver ant can be a symbolic relationship with humans as the fourth demesticated insect.
- Desired cooperation
-
- Control and management of invasive alien ants
- Behavioral research of ants and other insects
- Development of communication device with ants using acoustic signals
- Domestication research of the black Japanese weaver ants
-
Faculty of Science, Department of Zoology
- Professor
- Yuji TAKENOSHITA
- Research Field
Primatology, Anthropology, Zoo Sciences, Socio-Ecology, Conservation Ecology, African Studies
- Keyword(s)
Primates, Gorilla, Zoo, Biodiversity Conservation, Africa, Human Evolution
- Research theme
-
- Studies on feeding ecology and life history strategies in wild western lowland gorilla (Gorilla g. gorilla)
- Cooperative breeding among primates
- Evolution of non-reproductive aspect of primate and human sexuality
Outline of research activities




Primates (precisely non-human primates), are the animal group that shares the most similarities with humans. They show high levels of intelligence and social skills. Additionally, many primate species live in tropical and subtropical regions and are considered keystone species that play a fundamental role in maintaining tropical ecosystems. Researching the society and ecology of primates can provide us with valuable insights into the evolution and nature of humans. This knowledge can help us better understand ourselves, as well as contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the resolution of global environmental issues. My work involves studying the society and ecology of primates and other large and medium-sized mammals, mainly through field observations. I also examine human society from a zoological perspective and its evolution. Currently, my team and I are conducting long-term field research and conservation activities to protect wild gorillas in the tropical forests of Central Africa. We also conduct educational and animal welbeing activities in zoos and perform behavior observation research on Japanese macaques in Japan.
- Desired cooperation
-
- Development of ecological and behavioral data collection equipment and systems in tropical forests using ICT technology
- Practice of local ecosystem conservation activities through collaboration between researchers and citizens ( local community members)
- Zoo-based biodiversity conservation education activities
-
Faculty of Science, Department of Zoology
- Associate professor
- Atsushi NAKAMOTO
- Research Field
Animal Ecology, Behavioral Ecology, Conservation Science
- Keyword(s)
Fieldwork, Wildlife, Ecosystem services, Biocultural diversity
- Research theme
-
- Ecology of flying foxes
- Animal-plant interactions (seed dispersal and pollination)
- Ecology of urban wildlife
- Distribution and ecology of mammals in Okayama Prefecture
Outline of research activities



We focus on the ecology of wild animals, including endangerd species, and their function in the ecosystem using direct observation or research tools such as camera trap. We explore better conservation methods and way for a sustainable coexistence with people.

- Desired cooperation
-
- Ecological survey and conservation activities of endangered animals
- Wildlife management
- Citizen science
- Research on biocultural diversity (collaboration with cultural anthropology and folklore)
-
Faculty of Science, Department of Zoology
- Associate professor
- Ken TAKUMI
- Research Field
Neuroendocrinology, Reproductive physiology
- Keyword(s)
Postnatal development, Hormone, Brain
- Research theme
-
- Development of reproductive functions
- Effects of light-dark cycle on the onset of puberty
- Monitoring of reproductive status by steroid hormones in hair
Outline of research activities

Mammanlian reproductive status changes during postnatal development and aging. It can also be altered by environmental cues, stress or dysfunction of related organs. My research aims to clarify the factors and the mechanism which affect reproductive functions by using histological analysis on hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and measuring reproductive hormones. I am also working to establish methods to monitor reproductive status of wild animals by measuring steroid hormones in hair.
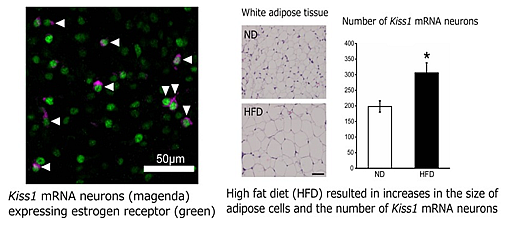
- Desired cooperation
-
- Histological analysis of peptides and mRNA localization
- Measurement of steroid hormones in hair
-
Faculty of Science, Department of Zoology
- Lecturer
- Mitsuo NUNOME
- Research Field
molecular phylogeography, population genetics
- Keyword(s)
wild animals, domestic Japanese quail, Japanese dormouse, genetic diversity
- Research theme
-
- reproductive, behavioral characteristics of Japanese quail
- Population genetics and phylogenetic study on wild animals
- Conservaton for threatened animals
Outline of research activities

Japanese quail are the second most reared animal in the world poultry industry (meat and egg production), after chickens. Although suitable environments to improve productivity of domestic quail have been studied, not much is known about their biological characteristics, such as whether they are monogamous or polygamous, how females and males are involved in child rearing, and how they select partners. A better understanding of these issues will contribute to further improvement of quail productivity, and we are conducting behavioral and genetic research by actually raising and observing quail.
We also conduct population genetic and phylogeographic studies to understand how wild animals adapt to and live in their habitats, with focuses on wild animals.
- Desired cooperation
-
- approaches to analyze defferences of color, color pattern, sounds presented by animals







