-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering
- Professor
- Masanori SEKI
- Research Field
Machine Design, Tribology
- Keyword(s)
Rolling Fatigue, Tribology, Machine Element, Peening
- Research theme
-
- Improvement in rolling contact fatigue life due to materials and surface treatments
- Influence of lubricant on rolling contact fatigue
- Application of cavitation peening
- Performance evaluation of plastic gears
Outline of research activities

Machine elements such as screws, gears, bearings, shafts, and springs are components needed for mechanisms. The performance improvement of machine elements is essential for that of the mechanical device. Therefore, in the machine design laboratory, we work toward the high performance and high strength of machine elements in terms of materials, machining, and surface treatments. Specifically, we are working on the performance evaluation of plastic gears using gear testing machines, the rolling contact fatigue life evaluation of bearings with a ball-on-disk contact tester, the sliding characteristic evaluation of steel using a high temperature tribometer.

- Desired cooperation
-
- Evaluation of rolling contact fatigue life of steel
- Evaluation of sliding characteristic of steel
- Performance evaluation of plastic gears
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering
- Professor
- Ryota HAYASHI
- Research Field
Vertebrate Paleontology, Bone Histology, Evolutionary Biology
- Keyword(s)
Dinosaur, Mammal, Bone Histology, Aquatic Adaptation, Ontogeny
- Research theme
-
- Dinosaur evolution and ecology
- Secondary adaptation of tetrapods to life in water
- Gigantism and dwarfism of vertebrates
Outline of research activities

Bone histology is the study of internal bone tissues, and provides important clues to physiological and ecological aspects of extinct animals such as the growth rate, longevities, potential metabolism and aquatic adaptation.
I am currently conducting researches on bone histology of large tetrapods (e.g., dinosaur, mammal and amphibians) to understand their gigantism, dwarfism and aquatic adaptations.
- Desired cooperation
-
- Researches on living vertebrates (e.g., ecology, anatomy, and pathology)
- Paleoenvironment researches based on geology
- Vertebrate paleontological researches
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering
- Associate professor
- Akihiro TAKEMURA
- Research Field
Plastic Deformation, Metal crystal Structure, Corrosion Proof
- Keyword(s)
Metal material, Material Property, Maching Process, Productivity
- Research theme
-
- Influence of maching on chemical property of material
- Influence of heat treatment on heat-transfer performance of material
- Reserch of metal maching performance
Outline of research activities




In the case of metal materials are machined, the surface of materials are plastic defomed. Cristal structure of metal surface is strained by plastic deformation. The crystal structure strain changes the chemical property of surface. This phenomenon is called a mechano-chemical reaction. We study the mechano-chemical reaction and the relationship of machining process and material property.

- Desired cooperation
-
- Improving the machinability of metal materials
- Anticorrosion engineering of metal surface treatment and processing
- Improvement of metallic materials productivity
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering
- Associate professor
- Chihiro KONDO
- Research Field
Internal Combustion Engine, Combustion, Instrumentation Engineering, Numerical Simulation
- Keyword(s)
Engine systems, Combustion, Alternative fuel,Waste Heat Recovery from Internal Combustion Engines
- Research theme
-
- Study on the combustion in engine systems and method of production and optimal usage of alternative fuels for vehicles and electricity generators
Outline of research activities



The engine is an essential piece of machinery that is used in vehicles, electricity generators, ships, and so on. However, fossil fuels are limited in their amount and engines exhaust carbon dioxide from the burning of hydrocarbon-based fuels, which is treated as a cause of global warming. Therefore, in order to deal with these problems, an alternative fuel is proposed that is comparable to fossil fuel in terms of fuel properties such as ignitability, calorific value, cold flow properties and oxidation, but which is environmentally friendly. In this laboratory, a study is conducted on the production and optimal usage of alternative fuels such as biofuel (e.g., biodiesel), gaseous fuel, and so on. Combustion technology for engine systems for low fuel consumption rate using natural gas and hydrogen is also studied.
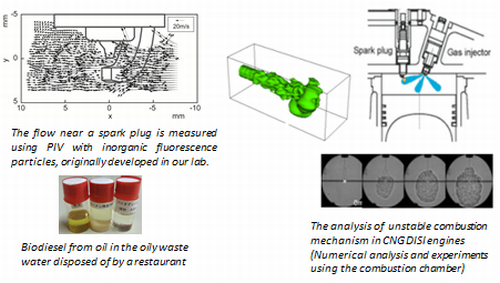
- Desired cooperation
-
- Development of higher output and higher thermal efficiency CNG engines (especially direct-injection spark-ignition CNG engines)
- Development of gas flow mesurement method using inorganic fluorescent particles (fluorescent PIV)
- The production method and evaluation method of bio-fuel especially made from waste oil in the oily wastewater
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering
- Associate professor
- Koji IWANO
- Research Field
Fluid engineering, Mechanical engineering, Chemical engineering, Environmental engineering
- Keyword(s)
Turbulence, Transport phenomena, Multiphase flow
- Research theme
-
- Scalar mixing in liquid-phase turbulent flows
- Momentum/Heat/Mass transport across wind-wave air-water interface
- Behavior of droplets and bubbles in turbulent flows
Outline of research activities



In order to improve the performance of various industrial devices and to make effective use of energy, it is important to understand and control the mechanisms of momentum, heat, and mass transport by turbulent flows. Understanding of turbulent transport phenomena is also essential for accurate prediction of meteorological phenomena. Our specific research topics include: experiments and numerical simulations to elucidate the mixing mechanism of scalars in liquid-phase turbulent jets; measurements of momentum, heat, and mass transport across wind-wave air-water interfaces to improve the prediction accuracy of typhoons; experiments to elucidate the behavior of droplets and bubbles in turbulent flows; and the development of novel devices (plasma actuators) to reduce fluid friction drag.

- Desired cooperation
-
- Turbulent transport phenomena in industrial and environmental processes.
- Development of novel fluid measurement methods for complex flow fields.
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering
- Associate professor
- Motoki TERANO
- Research Field
Manufacturing processing
- Keyword(s)
Metal Forming,Microsturucture control, Micro/nano forming, Tribology
- Research theme
-
- Development of local microsturucture control method
- Precision metal forming using CAE analysis
- Development of efficient fabrication method of functional surface by nano forming
Outline of research activities



The mechanical and electro-magnetic characteristics of metals are dependent on microstructures such as crystal orientation and grain diameter. In recent years, comprehensive studies have been carried out on thermo-mechanical control processing to improve physical properties of metallic materials without adding rare elements in order to save energy and resources. For example, high performance metals, such as ultrafine grain steel and magnetic steel, are developed by a combination of rolling and heat treatment. These metals exhibit uniform characteristics. However, it is more efficient if suitable characteristics can be generated at required positions. In our research, a new technology to control only material surface microstructure is being studied.
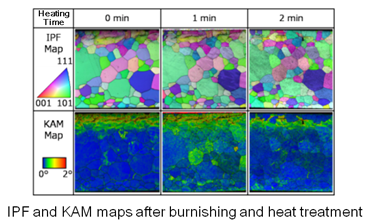
- Desired cooperation
-
- Local microsturucture control
- CAE analysis for metal forming
- Fabrication of functional surface by nano forming
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Professor
- Akihiro ORITA
- Research Field
Organic Chemistry, Organometallic Chemistry, Organic Materials
- Keyword(s)
Organic Synthesis, Acetylenes, Fluorescence, Solar Cells, Sulfones, Organostannanes
- Research theme
-
- Syntheses of novel expanded π-systems
- Syntheses of organic fluorescent and semi-conducting materials
- Syntheses of organic dyes for solar cells
- Syntheses of environmentally benign organotin catalysts and organic photocatalysts and their applications to organic syntheses
Outline of research activities


1. Organic light-emitting materials for OLEDs or dyes for OPVs are developed.
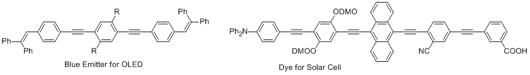
2. Novel antiaromatic compounds such as Sondheimer-Wong diynes and diarenopentalenes are developed as new types of organic materials.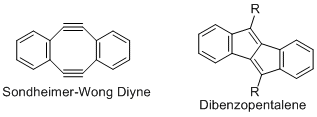
3. Organic syntheses using organotin cluster as catalysts are developed.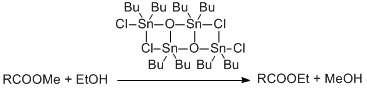
- Desired cooperation
-
- Organic synthesis
- Organic materials
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Professor
- Hiroyuki HIRANO
- Research Field
Chemical Engineering, Transport Phenomena, Numerical Calculation
- Keyword(s)
Fluid flow and Heat transfer, Microreactor, Simulation
- Research theme
-
- Alternating flow in micro-channel
- Natural convection by temperature and/or concentration gradient
- Interfacial disturbance by Marangoni effect
- Solar energy storage by salinity-gradient solar pond
Outline of research activities

Numerical and experimental studies on transport phenomena, e.g. chemical reaction in beaker, indoor environment with air conditioner, natural environment, fluid flow and heat transfer in industrial equipment
■ patent number: 4931065
title of the invention: collision micro mixer
objective: increasing the chemical reaction efficiency by the collision of water and organic phases in the micro-channel
■ patent number 5504526
title of the invention: formation of slug flow with micro-reactor
objective: increasing the chemical reaction efficiency with the vortices generated by continuously changing the shapes of water and organic phases inside the micro-channel with zigzag wall
- Desired cooperation
-
- Development of high-efficiency micro-reacter
- Development of solar energy storage system
- Solution of the problem on transport phenomena
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Professor
- Jun OSHITANI
- Research Field
Chemical Engineering, Particle Technology
- Keyword(s)
Powder and Colloid
- Research theme
-
- Dry separation using gas-solid fluidized beds
- Advanced powder handling for chemical manufacturing
- Application of surfactant-free colloids
Outline of research activitiesPowder and colloid are important for manufacturing processes. We study on fundamentals and applications of powder and colloid to contribute to the manufacturing processes as engineers. For example, we developed dry separator using gas-solid fluidized beds for waste treatment and mineral processing.

- Desired cooperation
-
- Application of the dry separator
- Developing the new powder handling methods
- Application of the surfactant-free colloids
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Professor
- Makoto TAKEZAKI
- Research Field
Colloidal chemistry, Solution chemistry, Photochemistry
- Keyword(s)
Nanoparticles, Micelles, Photoinduced reactions, Absorption and emission spectroscopy
- Research theme
-
- Synthesis and characterizations of non-spherical nanoparticles
- Fluorescence enhancements by nanoparticles
- Photoinduced reaction on the micellar and vesicular systems
Outline of research activitiesMetal nanoparticles show unique properties that are different from those of bulk metals. These properties are dependent on their shapes and sizes. We prepare nanoparticles with various shapes and ones with narrow size distributions. Fluorescence intensities are enhanced at the acuate front ends of nanoparticles and/or at the gaps between nanoparticles. The protective agents of nanoparticles, such as ligands, polymers and surfactants, are exchanged for fluorophores easily to adsorb the surfaces of nanoparticles.
The photoinduced reactions on the micellar and vesicular systems and the properties of the micellar and vesicular systems are studied.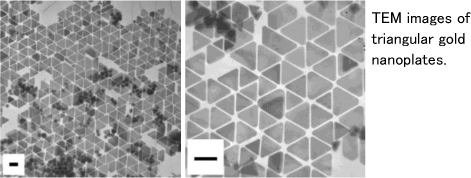
- Desired cooperation
-
- Syntheses of metal nanoparticles
- Characterizations of micelles, vesicles and aggregates
- Spectroscopic characterizations, etc.
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Professor
- Yoshihiro KUSANO
- Research Field
Inorganic Material Chemistry, Chemistry of Ceramics
- Keyword(s)
Ceramics, Transition Metal Oxides, Pottery and Porcelain, Bizen Stoneware
- Research theme
-
- Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Japanese Traditional Ceramics
- Synthesis and Properties of Novel Transition Metal oxides
Outline of research activitiesThe characteristic reddish color pattern called hidasuki appears where the rice straw is in direct contact with the clay because the rice straw supplies potassium that reduces the melting point of the ceramic surface and thereby converts the contact area into a site for the interesting reactions to take place. The sticklike mullite (3(Al,Fe)2O3・2SiO2) particles, the major phase formed in the absence of rice straw, was replaced by corundum (α-Al2O3), hematite (α-Fe2O3), and others in the surface region of about 50 μm-thick. The corundum precipitated as hexagonal platelike crystals, and on the edges of these crystals the hematite grew epitaxially.
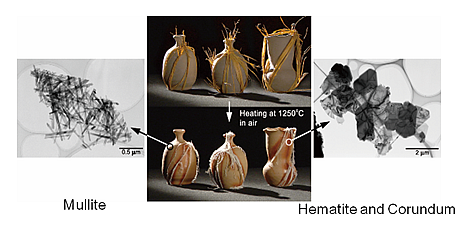
- Desired cooperation
-
- Microstructural observations of metals and ceramics
- Formation mechanizm of color patterns on pottery and Porcelain
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Professor
- Yoshiko MORIYAMA
- Research Field
Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Protein Chemistry
- Keyword(s)
Surfactant, Secondary Structure of Protein
- Research theme
-
- Interactions of Surfactants with Proteins and Polypeptides
- Interaction of Surfactants with Proteins Denatured by Urea and Heat treatment
Outline of research activities

The interactions of surfactants with proteins have been widely studied. Recently, an attention has been paid to the effects of surfactants on the secondary structural changes of proteins denatured by another denaturing factor.

- Desired cooperation
-
- Physicochemical Properties of Surfactant Solutions
- Secondary Structural Changes of Proteins
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Professor
- Yuichi KOGA
- Research Field
Biotechnology, Biochemistry, Bioproduction
- Keyword(s)
Protein, Enzyme, Microbe, Hyperthermophile
- Research theme
-
- Structure-function relationships of proteins from extremophiles.
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) degrading enzymes
- Industrial application of thermostable proteases, etc.
Outline of research activitiesOrganisms that can grow in a “extreme environment”, such as the high temperature environment, are called extremophiles. These organisms have unique biomolecules that are adapted to the environment in which they grow. A typical example are enzymes that catalyse most of chemical reactions in cells. General enzymes lose their molecular structure and function in high temperatures (e.g., 80°C), however hyperthermophiles, which can grow at 100°C, have enzymes with a unique structure that can maintain their function even at 100℃. Proteins from extremophiles can enable new chemical reactions that have not been possible with normal enzymes. We will conduct research to elucidate the structure and function of extremophiles, and apply them to industrial applications.

- Desired cooperation
-
- Isolating microorganisms and enzymes from local resources (fermented foods, unique environment etc.)
- Development of industrial application of enzymes.
- Bioproduction and biodegradation.
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Associate professor
- Naoki NAGATANI
- Research Field
Analytical chemistry, Biotechnology
- Keyword(s)
Biosensor, Micro・nanobioprocess
- Research theme
-
- Development of biosensor
- Development of sensor using electro chemistry
- Development of paper based biosensor
Outline of research activities
Biosensors using enzyme and antibody and biochips for using biosensor have been developed. For example, chemical agent sensor based on inhibition of enzyme activity and the RT-PCR biochip for rapid detection of COVID-19 have been studied.

- Desired cooperation
-
- Development of rapid and easy biosensor.
- Development of new sensor based on biological function
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Lecturer
- Ryosuke MAKI
- Research Field
Inorganic chemistry, Ceramic materials
- Keyword(s)
High-temperature structural materials, Iron oxides, Synroc
- Research theme
-
- Development of a new synthesis method forε-Fe2O3
- Investigation for new refractory materials
- Investigation of synroc solidification technique
Outline of research activities

Recently, ε-Fe2O3 has attracted interest because of its magnetic potentiality, but there are some difficulties to straightforwardly obtain the pure/single ε-Fe2O3 phase. We have found that ε-Fe2O3 crystallizes epitaxially on crystals of mullite in our study on a Japanese traditional stoneware called “Bizen” . Since the particle morphology of ε-Fe2O3 and the relative ε-Fe2O3-to-mullite crystallographic orientation strongly depend on the oxygen partial pressure during firing and the temperature range, the formation conditions is very complicated. We believe that elucidating the formation mechanism of ε-Fe2O3 will contribute to the development of novel magnetic materials.
We are also working on the development of Al-B-C high-temperature structural materials. Ternary metal borocarbides, Al3BC3, have been considered as promising candidates for lightweight structural components. We have succeeded in synthesizing hexagonal plate-like Al3BC3 particles by a simple synthesis method, and the sintered sample exhibited anisotropic mechanical properties and higher bending strength due to particle orientation. Currently, we are proceeding with various physical property measurements.- Desired cooperation
-
- Development of a new synthesis method forε-Fe2O3
- Investigation for new refractory materials
- Investigation of synroc solidification technique
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry
- Lecturer
- Yasuhiro OKUDA
- Research Field
Organic Synthesis, Organometallic Chemistry, Theoretical Calculation
- Keyword(s)
Organic Synthesis, Reaction Design, Catalytic Transformation, Organic Material, Pharmaceutics
- Research theme
-
- Development of New Reactions Accelerated by Transition-Metal Catalysts
- Synthesis of Bioactive Compounds
- Design and Synthesis of Organic Materials
Outline of research activitiesOur laboratory focused on a phosphoryl (Ph2P(O)) group’s chemistry as an electron-withdrawing and removable protecting group on terminal alkynes, development of new reation and synthesis of functional molecules are currently investigated. For example, we demonstrated a process-controlled regiodivergent synthesis of triazole derivatives with bromo(phosphoryl)ethyne as common starting material, an alternative synthesis of commercially available pharmaceutical molecule was also succeeded (Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 5099–5103.)
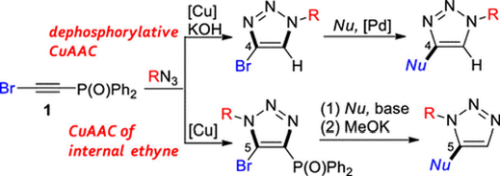
 More recently, we synthesized novel π-extended aromatic amines from ynamine (= alkynylamine), and further applications to luminescence, photovoltaics and hole-transporting materials are in progress.
More recently, we synthesized novel π-extended aromatic amines from ynamine (= alkynylamine), and further applications to luminescence, photovoltaics and hole-transporting materials are in progress.
- Desired cooperation
-
- Organic sythesis, drug discovery and material design employing ynamine (= alkynylamine) as a common starting material
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Architecture
- Professor
- Fuminori HIRAYAMA
- Research Field
Architectural Design
- Keyword(s)
user participation design, user evaluation,workshop, public cultural facilities
- Research theme
-
- User Evaluation of Public Cultural Facilities
- Analysis of user opinions and verification of effectiveness of user participation design
- Functional changes in public cultural facilities
Outline of research activities





In the design of public cultural facilities, there are an increasing number of examples of design methods that incorporate the users’ ideas at the architectural design stage in order to promote active use.
Our laboratory has collected 70 cases of participatory design from all over Japan. The following participatory design practices were implemented in our laboratory, and the effectiveness of participatory design was verified through analysis of user opinions and post-completion evaluations of these practices.
・Kudamatsu City Community Exchange Center (2013)
・Okayama Prefectural Doctor’s Hall (2015)
・Sanagouchi Village Office (2017)
・Kashiwa City Southern Neighborhood Center (2018)
- Desired cooperation
-
- Public facility planning and design
- User-participatory design practices
- User evaluation analysis of public facilities
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Architecture
- Professor
- Hiroyuki HOTTA
- Research Field
Foundation Engineering, Geotechnical Engineering, Disaster Engineering
- Keyword(s)
Foundation, Ground, Performance Evaluation, Disaster Survey
- Research theme
-
- Deformation of ground and structures during construction and usage of buildings
- Performance evaluation and reuse of existing piles
- Disaster survey and analysis of buildings and foundations
Outline of research activities



In order to ensure safety during construction and to assure quality and performance of buildings, I am conducting research on methods to predict and to evaluate deformation of ground and structures accurately.
Also, to reduce cost, period, and environmental load of re-building, I am researching survey or evaluation methods of existing piles and foundation design reusing them.
In case of disasters such as earthquakes or heavy rains, I quickly survey on site, analyse the cause of damage, and utilise the results for subsequent disaster prevention and mitigation.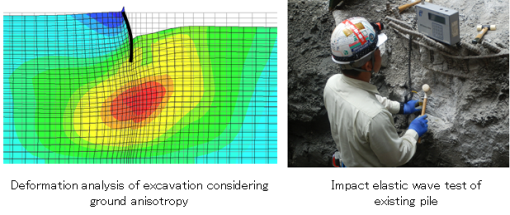
- Desired cooperation
-
- Rationalisation of foundation design and underground construction
- Disaster survey and diagnosis, restoration and reconstruction plan
- Research on optimization methods in the life cycle of buildings
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Architecture
- Professor
- Kazuhiko SAKAMOTO
- Research Field
Environmental Engineering, Building Services Engineering
- Keyword(s)
Environmental Planning, Building Services, M&E Engineering Design, Energy Conservation
- Research theme
-
- Study for the New Design method of Water Supply System based on the Dynamic Calculation Method of the Water Supply Demands
- Research on Optimization of Indoor Thermal Environment
- Study fot the most Suitable Operation method about Building Services
Outline of research activities




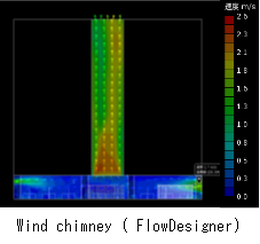 One of the important roles of the Building Services Engineering, the follow things must be compatible.
One of the important roles of the Building Services Engineering, the follow things must be compatible.
· Building comfort environments for users.
· Adopting energy conservation techniques for the global warming-control measures.
Air Conditioning System : Explaining the effect of natural ventilation by the Computational Fluid Dynamics program.
Plumbing System : Recently, the follow things are realized.
· Water consumption decreases by using water saving plumbing fixtures.
· Booster pump systems increse.
Therefore, I explain the instantaneous flow rates and study the new design method for water supply system.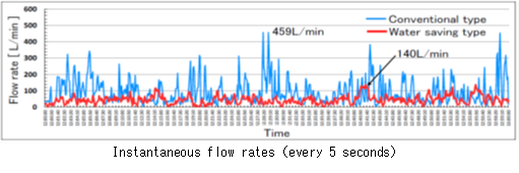
- Desired cooperation
-
- Development of the new water supply system
- Energy conservation chek of Building Services
- Development of practical use methods of renewable energy
-
Faculty of Engineering, Department of Architecture
- Professor
- Keiji NAKANISHI
- Research Field
Eathquake-Resistant Structure, Antiseismic Reinforcement
- Keyword(s)
Reinforced concrete,Steel structure,Steel-reinforced concrete,Base isolation structure,Seismic control design, Antiseismic reinforcement,Optimum design
- Research theme
-
- Tublar truss structure in steel
- Wooden grid wall
- Base isolation and seismic control design
Outline of research activities



My spetial field of study is earthquake resistant structure. The way of my study is at first understanding of destruction mode and strength of structure by experiment , and next establishing design method by simulating the experimental results by analysis.
In 2015 I took up my new post of professor of Okayama University of Science, I was beginning of study of Tublar truss structure in steel with locally company. And in 2016 I was beginning study of Base isolation structure and Seismic controle structure by using the small vibration table.
I am planning to study of new structure of minimizing damage under large eathquake expected in the near future.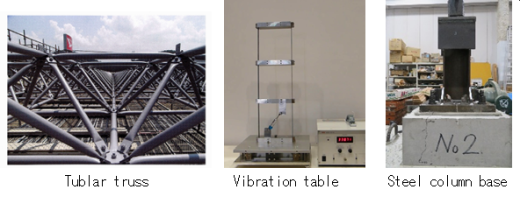
- Desired cooperation
-
- Experimental study of Reinfoced concrete,Steel structure.
- Experimental study of Base isolation structure.
- Analytical study of Optimum design.







